Choosing a new air conditioning system is a significant decision for any homeowner. You want comfort, efficiency, and a solution that fits your specific needs and budget. Two popular contenders often come up: the versatile mini-split system and the traditional central air conditioning unit. While both aim to cool your home, they operate differently and offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed choice that will keep you cool and comfortable for years to come. This guide will break down the matchup between mini-split vs central air, helping you determine the ideal cooling solution for your living space.
Understanding the Core Differences: How They Work
Before diving into the pros and cons, it’s essential to understand the fundamental operational differences between mini split vs central air.
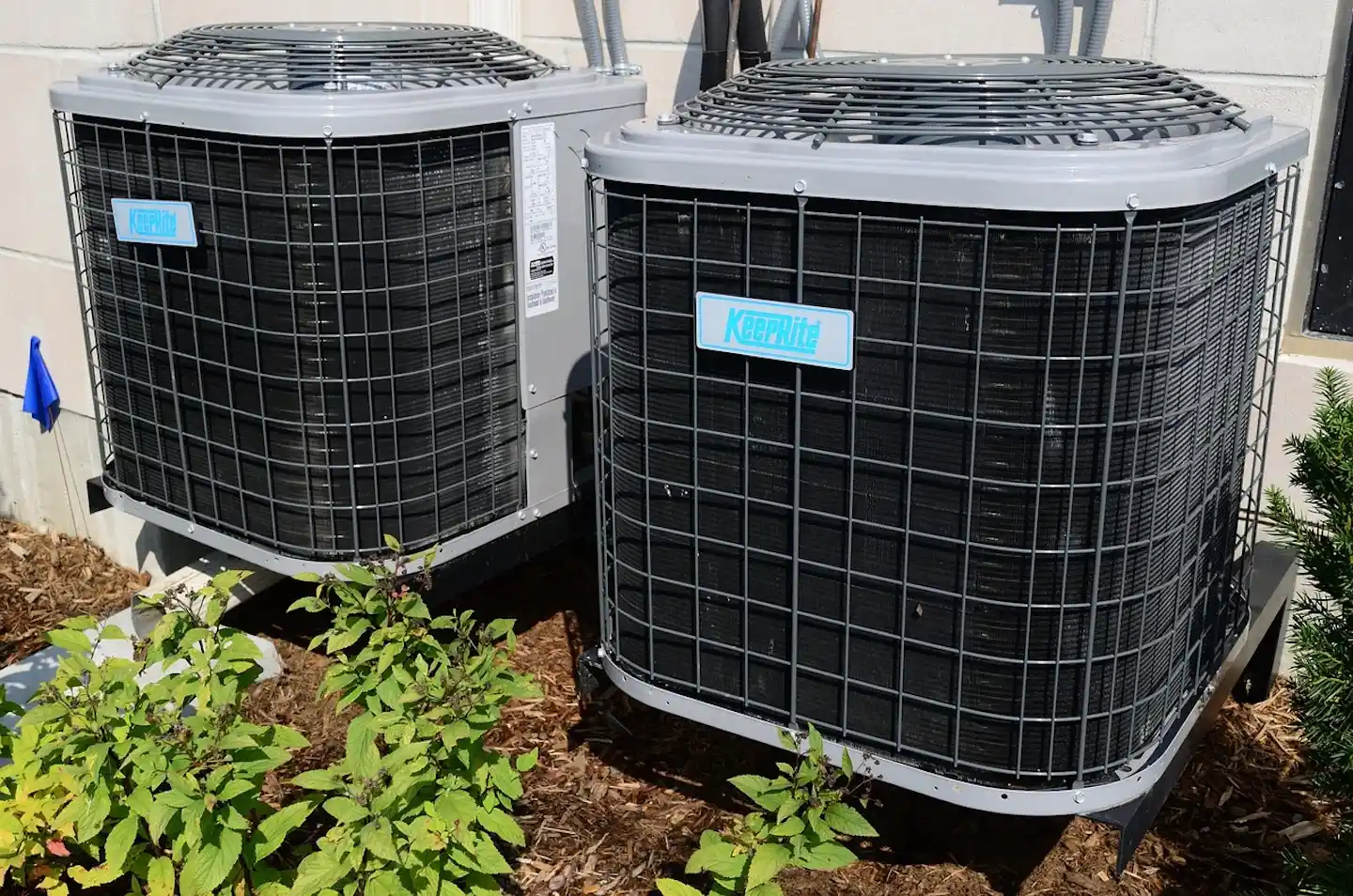
Central Air Conditioning
This is the system most people are familiar with. A central air conditioner typically uses a large outdoor unit (condenser) connected to an indoor unit (air handler, often part of your furnace). The air handler distributes cooled air throughout the entire house via a network of ducts and vents. A single thermostat, or sometimes a zoned system with multiple thermostats, controls the temperature for the whole home or specific large areas. The air is cooled at a central point and then pushed through the ductwork to each room. This system is designed for whole-house cooling and often integrates with your heating system.
Mini-Split Air Systems
Mini-split, also known as ductless or ductless mini-split systems, offer a more decentralized approach to cooling (and often heating). Like central air, they have an outdoor compressor/condenser unit, but instead of one large indoor air handler, they connect to one or more compact indoor air handling units. These indoor units are typically wall-mounted, ceiling-recessed, or even floor-standing, and each one cools a specific room or “zone.” A thin conduit containing the refrigerant lines, power cable, and condensate drain connects the outdoor unit to the indoor units, requiring only a small three-inch hole through the wall. Each indoor unit has its own thermostat, allowing for independent temperature control in different zones.
Installation: Effort, Invasiveness, and Initial Setup
The installation process and requirements vary significantly between central air and mini-split systems, impacting both cost and convenience.
Central Air Installation
If your home already has existing ductwork in good condition, replacing an old central air unit with a new one can be relatively straightforward. However, if your home lacks ductwork (common in older homes or those with non-forced air heating like radiators or baseboards), installing a new central air system becomes a major undertaking. This involves fitting extensive ductwork throughout your walls, ceilings, or attic, which can be invasive, time-consuming, and significantly more expensive. Even with existing ductwork, ensuring it’s properly sized, sealed, and clean is crucial for efficient operation, potentially adding to the initial workload.
Mini-Split Installation
Mini-split systems shine when it comes to installation flexibility and ease, particularly in homes without existing ductwork. The lack of extensive ductwork means installation is far less invasive. The primary requirement is mounting the indoor units and connecting them to the outdoor unit via the small conduit. This makes them an excellent choice for additions, retrofitting older homes, or targeting specific areas that are difficult to cool. A single-zone (one indoor unit) mini-split can often be installed in a day, while multi-zone systems (multiple indoor units connected to one outdoor unit) will take longer but are still generally quicker and less disruptive than installing a full central air system with new ductwork.
Efficiency and Zoning: Tailoring Your Comfort and Energy Bills
Energy efficiency and the ability to control temperatures in different areas are critical factors that directly impact your comfort and long-term operating costs.
Central Air Efficiency and Zoning
Modern central air conditioners have become significantly more energy-efficient, with SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings commonly ranging from 14 to 22+. However, a significant potential for energy loss in central air systems comes from the ductwork. Leaky, poorly insulated, or improperly sized ducts can account for up to 30% of energy consumption for space conditioning. While central air systems can be equipped with zoning capabilities (using dampers in the ductwork and multiple thermostats to control different areas of the house), these systems can add considerable expense and complexity. Without zoning, you’re cooling the entire house to the same temperature, even rooms you’re not using, which can lead to wasted energy.
Mini-Split Efficiency and Zoning
A mini-split is generally highly energy-efficient. Because the cooled air is delivered directly into the room from the indoor unit, there are no energy losses associated with ductwork. Many mini-split models boast very high SEER ratings, some exceeding 30. Furthermore, the inherent design of mini-split systems facilitates zoning. Each indoor unit operates independently, allowing you to cool only the occupied rooms and set different temperatures based on individual preferences. This targeted cooling can lead to substantial energy savings compared to cooling an entire home with a central system, especially if only certain areas are regularly used. Many mini-splits also feature inverter technology, which allows the compressor to adjust its speed based on demand, further enhancing efficiency and providing more consistent temperatures.
Cost Considerations: Upfront Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
The financial aspect is a crucial part of the decision-making process, encompassing both the initial purchase and installation costs, as well as ongoing operational and maintenance expenses.
Central Air Costs
The upfront cost of installing central air can vary widely. If replacing an existing unit and using current ductwork, the cost can be moderate. However, if new ductwork installation is required, the initial investment can be significantly higher, potentially ranging from $5,000 to $12,000 or more, depending on the home’s size and complexity. Annual maintenance, including professional check-ups and filter replacements, is essential. Duct cleaning, recommended every 3-5 years, adds another recurring expense. While newer central units are more efficient, energy bills can still be substantial, especially for larger homes or in hotter climates, particularly if the ductwork isn’t optimal.
Mini-Split Costs
The initial cost of a mini-split system depends on the number of zones (indoor units) needed. A single-zone system might cost less than a new central air installation (especially if ductwork is needed for the central system), typically ranging from $2,000 to $6,000 for one zone. However, for a multi-zone system to cool an entire house, the upfront cost can be comparable to or even exceed that of a central air system, potentially reaching $10,000-$15,000 or more. Maintenance involves regularly cleaning the filters on the indoor units (often monthly) and ensuring the outdoor unit is clear of debris. Professional servicing is also recommended annually. The significant advantage lies in lower operating costs due to higher efficiency and zoned cooling, potentially leading to substantial long-term savings on energy bills.
Pros and Cons at a Glance: Making the Final Call
To help summarize, here’s a quick rundown of the primary advantages and disadvantages of each system:
Central Air Conditioning Systems
Pros:
- Invisible Operation: Ductwork and air handlers are hidden, with only subtle vents visible, maintaining room aesthetics.
- Whole-House Uniformity: Provides consistent cooling throughout the entire home from a single system.
- Often Lower Upfront Cost (with existing ductwork): If suitable ductwork is already in place, replacing or installing a central unit can be more cost-effective initially.
- Air Filtration for the Whole Home: Central systems can incorporate advanced air filters, improving air quality throughout the house.
- Good for Large Homes: Efficiently cools larger, open-plan homes where individual zoning is less critical.
Cons:
- Requires Ductwork: Installation is invasive and expensive if ductwork isn’t present or needs significant repairs.
- Energy Loss Through Ducts: Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can lead to significant energy inefficiency.
- Less Flexible Zoning: Standard systems cool the entire house; adding sophisticated zoning increases cost and complexity.
- Can Be Noisy: The outdoor unit and sometimes the air handler can generate noticeable noise.
- One Thermostat for All: Less individual comfort control for different rooms or occupants without investing in a zoning system.
Mini-Split Air Systems (Ductless)
Pros:
- No Ductwork Needed: Ideal for homes without existing ducts, additions, or specific problem areas. Installation is less invasive.
- High Energy Efficiency: Direct air delivery means no duct losses, and many units have very high SEER ratings. Inverter technology further optimizes energy use.
- Flexible Zoning and Individual Control: Each indoor unit has its own thermostat, allowing for personalized comfort and energy savings by cooling only occupied zones.
- Quiet Operation: Indoor units are typically very quiet, and outdoor units are often quieter than traditional central AC condensers.
- Can Provide Heating: Many mini-split models are heat pumps, offering both cooling and efficient heating.
Cons:
- Visible Indoor Units: Wall-mounted, ceiling, or floor units are visible in the room, which may not appeal to all homeowners.
- Higher Upfront Cost for Whole-Home Coverage: Equipping an entire house with multiple indoor units can be more expensive initially than a basic central air system (if ductwork exists).
- Regular Filter Maintenance per Unit: Each indoor unit has a filter that needs regular cleaning (often monthly).
- Distribution in Larger, Complex Rooms: A single indoor unit might struggle to evenly cool very large or irregularly shaped rooms without careful placement or multiple units in that space.
- May Require Multiple Outdoor Units: Very large homes or specific configurations might require more than one outdoor condenser.
Ultimately, the choice between mini-split and central air conditioning depends on your specific circumstances. Feeling unsure about the best fit for your home?
Contact us today! Our team of HVAC professionals is here to provide expert, tailored advice and help you select the perfect air conditioning system that will best serve your needs and keep you comfortable all year round!